[SD][ML] ControlNet in StableDiffusion: A Comprehensive Guide
Overview
ControlNet is an innovative addition to the StableDiffusion model that enhances the model’s ability to generate high-quality images with specific control over the content and structure. This guide delves into the fundamentals of ControlNet, how it works, implementation details, and training your own ControlNet. The following sections provide an in-depth look at each aspect of this powerful tool.
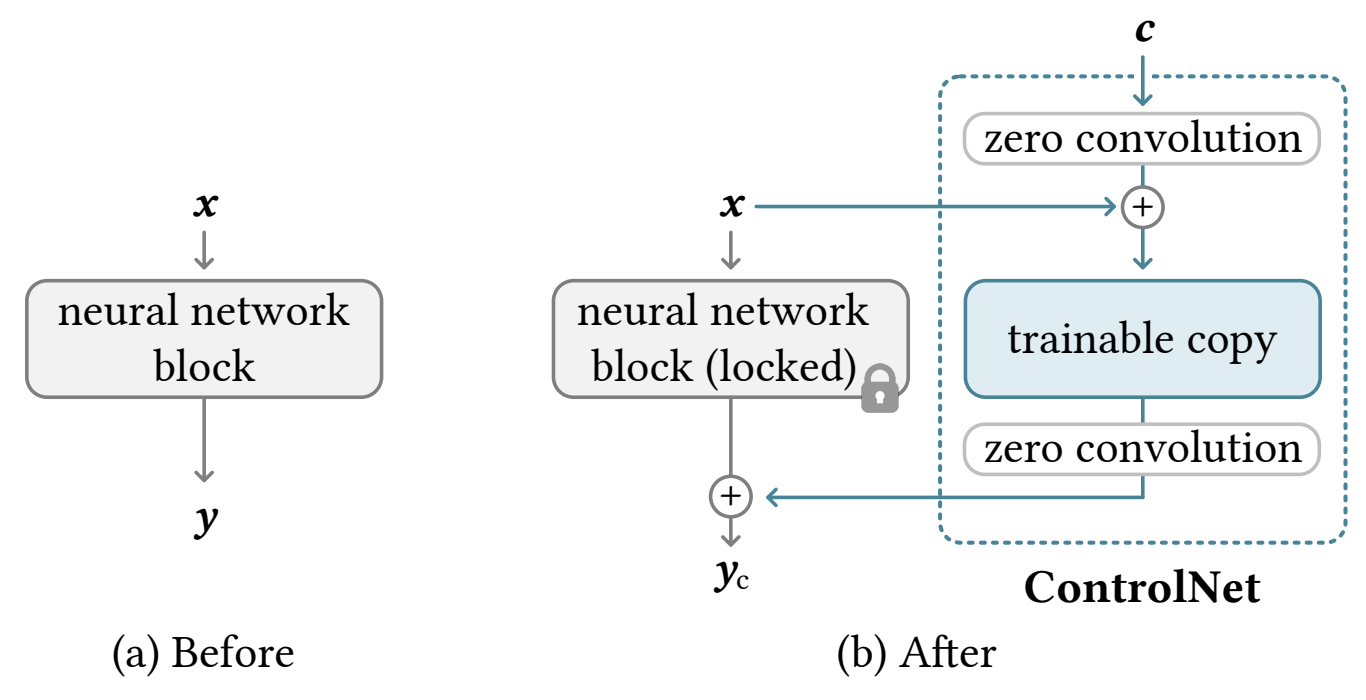 source: https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543
source: https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543